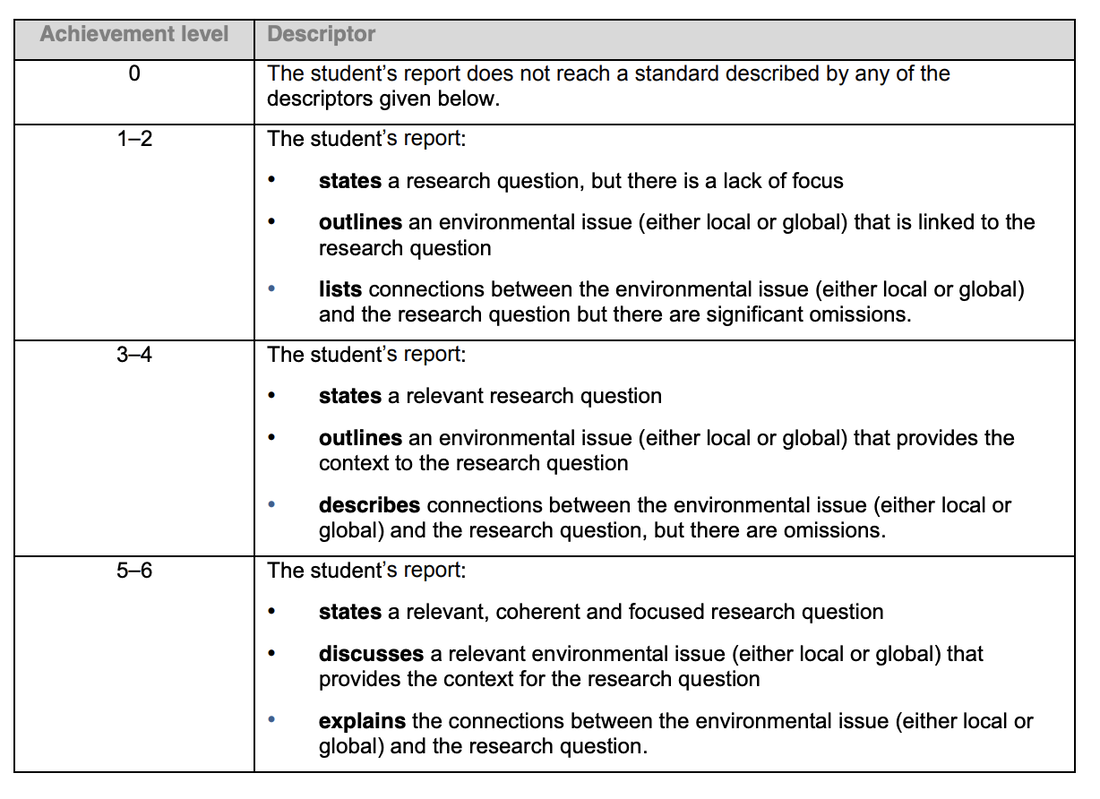
Identifying the context

This criterion assesses the extent to which you establish and explore an environmental issue (either local or global) for an investigation and develops this to state a relevant and focused research question.
This criterion assesses the development of the purpose of the study. You will be expected to show an understanding of the broader environmental issue and then develop you idea for a focused research question.
This criterion assesses the development of the purpose of the study. You will be expected to show an understanding of the broader environmental issue and then develop you idea for a focused research question.
Identifying the context (6)
The environmental issue is the overarching reason for your lab. (Think is it in the book). EVERYTHING IS LINKED BACK HERE!
Large ideas could include but are not limited to:
Environmental Issue:
This is a great document from Science Sauce to help select your topic
The environmental issue is the overarching reason for your lab. (Think is it in the book). EVERYTHING IS LINKED BACK HERE!
Large ideas could include but are not limited to:
- increased use of fossil fuels
- desertification
- eutrophication of water due to farming techniques
- loss of biodiversity
- over population/ urbanization
- over consumption of ground water
Environmental Issue:
- Identify an environmental issue in relation to your RQ (Should be done first!)
- Discuss the environmental issue in the context of your Research Question
- Develop a range of arguments within the focus of the issue
- Explain how the issue is connected to your Research Question
This is a great document from Science Sauce to help select your topic
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
Research Question:
- Should arise from a broader area of environmental interest (the context), so that in conjunction with evaluating the research process and findings of your study, you will be able to discuss the extent to which the study applies to the environmental issue that interests them at a local, regional or global level (the application)The research questions is clearly stated and precisely formulated.
- Explain the broader issue and then distill this to create a focused research question
- Has relevance to a broader issue but is at a meaningful scale for the time frame investigated
- Is it testable?
- Does is contain both independent and dependent variable?
- Is it focused and clear (do people know exactly what you are trying to do without asking questions)?
- Research question includes scientific name of organism, if relevant (Genus species).
- The research question can be used to formulate a hypothesis predicting the relationship between the DV and IV.
The discussion should lead you to develop creative thinking and novel solutions, or to inform current political and management decisions relating to the issue. For example, if you carry out a study on the impact of wind turbines that have been erected in the vicinity of your school, you may suggest solutions for the erection of wind turbines in other areas based on your findings.
Whatever you choose, should have a local or global connection somewhere specific that you are looking.
Example: Urbanization of the Dallas, TX, USA metro area is causing and increasing demand for water.
Warnings: Narrow your focus from overly broad issues to something specific to a country or local connection.
Examples:
- Broad: Climate Change
- More Focused: The destruction of the Trinity River Deciduous Forest in Dallas, TX, USA due to urbanization.
- Broad: Air pollution
- More focused: Use of coal plants in Lima, Peru and their energy choices
WHY?! Specific, clear, know what you are going to do without reading it, independent and dependent variables are clear.
Background:
- Explain everything the reader would need to know before doing the investigation?
- Explain the science behind the investigation? The Why and how of it working?
- Cite your sources (in text and work cited)?
- Explain how the science is connected to your investigation research idea?
- The background sets the research question into context.
- Justify the connection between your study and the bigger problem that was the stimulus for your investigation
- Background information provide sufficient information about the environmental context
- Appropriate and relevant background correctly described and explained.
- Citations relevant to the research question are used.
- Background information is used to form a hypothesis.
Local/Global Connection:
- Provide the reader with an understanding of how the RQ and issue are connected to a local and or global environmental issue
- Clearly explain how these connections are relevant to your RQ
- Provide enough background information for the reader to understand these connections
If you are using any living organisms, or products from living organisms, such as seeds from a certain plant, give the most precise name you can and give the scientific name if possible (e.g. Phaseolus vulgaris for kidney beans).
The second and third in a series from Science Sauce about Choosing Your Topic and Writing Your Report