topic 7: ENERGY CHOICES AND SECURITY
 image from www.inflexwetrust.com
image from www.inflexwetrust.com
The current cycle of global warming is changing the rhythms of climate that all living things have come to rely upon. What will we do to slow this warming? How will we cope with the changes we've already set into motion? While we struggle to figure it all out, the face of the Earth as we know it—coasts, forests, farms, and snow-capped mountains—hangs in the balance.
In this unit you will evaluate the role of greenhouse gases, the effects of rising global temperatures and the arguments associated with global warming. This issue involves the international community working together to research and reduce the effects of global warming.
This unit is a minimum of 4 hours.
In this unit you will evaluate the role of greenhouse gases, the effects of rising global temperatures and the arguments associated with global warming. This issue involves the international community working together to research and reduce the effects of global warming.
This unit is a minimum of 4 hours.
Significant Ideas:
- There is a range of different energy sources available to societies that vary in their sustainability, availability, cost and socio-political implications.
- The choice of energy sources is controversial and complex. Energy security is an important factor in making energy choices.
Big questions:
- What strengths and weaknesses of the systems approach and the use of models have been revealed through this topic?
- To what extent have the solutions emerging from this topic been directed at preventing environmental impacts, limiting the extent of the environmental impacts, or restoring systems in which environmental impacts have already occurred
- What value systems can you identify at play in the causes and approaches to resolving the issues addressed this topic?
- How does your own value system compare with others you have encountered in the context of issues raised in this topic.
- How are the issues addressed in this topic of relevance to sustainability or sustainable development?
- In what ways might the solutions explored in this topic alter your predictions for the state of human societies and the biosphere some decades from now?
- How does the systems approach help our understanding of energy choices and security?
- Why do countries lack energy security?
- Why do some societies continue to use fossil fuels despite the damage they do to the environment?
- How do environmental value systems affect the choice of energy supply:
- Compare your environmental value systems with at least two other value systems in relation to energy consumption
- To what extent are global energy choices sustainable?
- How might energy choices evolve in the next decade?
Knowledge and Understanding
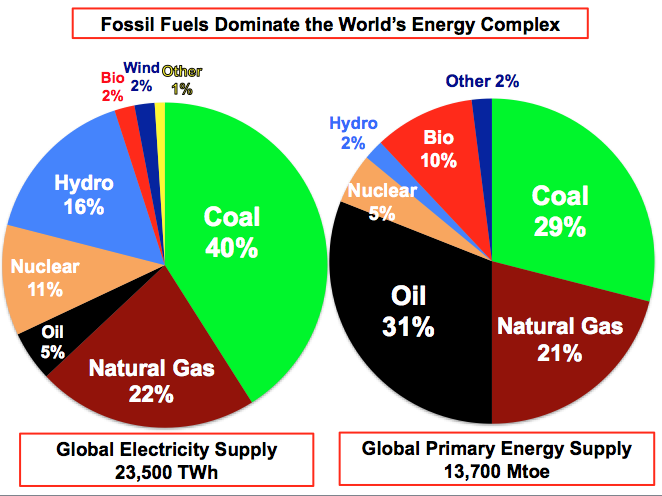
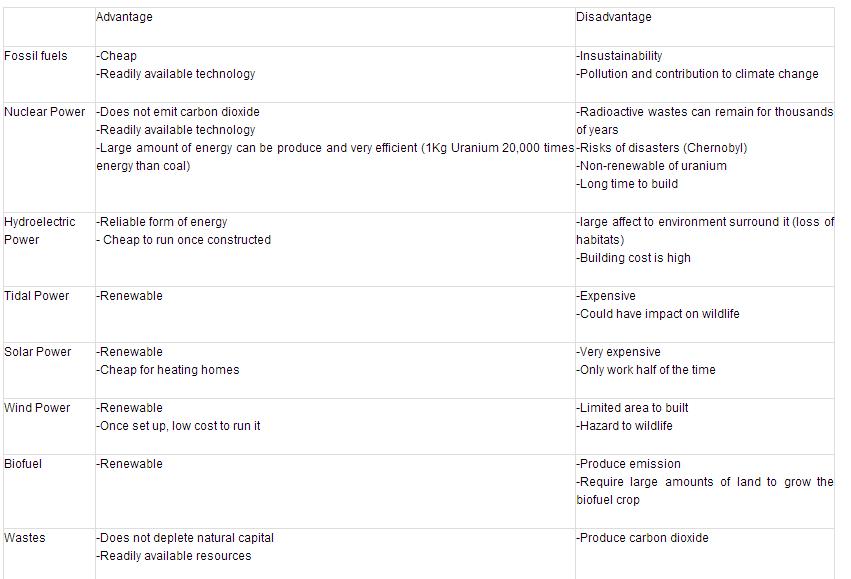
7.1.U1 Fossil fuels contribute to the majority of humankind’s energy supply, and they vary widely in the impacts of their production and their emissions; their use is expected to increase to meet global energy demand.
[Strengths and weaknesses of the use of a fossil fuel, of a renewable source of energy, and of nuclear power should be considered.]
[Strengths and weaknesses of the use of a fossil fuel, of a renewable source of energy, and of nuclear power should be considered.]
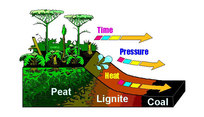
Fossil fuels are fuels formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms, containing energy.
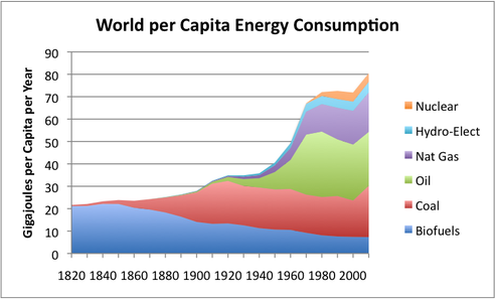
Fossil fuels were formed from the dead and decaying remains of prehistoric living organisms millions of years ago. Intense heat and pressure inside the different layers of earth transformed these dead remains into modern day's fossil fuel reserves. The fossil fuels are energy rich carbon compounds and hydrocarbons such as coal, natural gas and petroleum. The technological advances in the 20th century made possible the extraction of fossil fuels from the earth commercially viable. All our modern transportation and industry development process have been made possible because of the discovery and extraction of fossil fuels. More than three quarters of the world's energy consumption comes from fossil fuels. Of this approximately, 40% of fossil fuels are used in petroleum form, 15 % in natural gas form and 8 % in coal form. Fossil fuels are the main backbone of the industrialization but they have contributed to the burden of environmental pollution significantly. This has resulted in greenhouse gases, acid rain and global climate change. The massive demand for fossil fuels has resulted in depletion of their deposits at an alarming rate..
Fossil fuels were formed from the dead and decaying remains of prehistoric living organisms millions of years ago. Intense heat and pressure inside the different layers of earth transformed these dead remains into modern day's fossil fuel reserves. The fossil fuels are energy rich carbon compounds and hydrocarbons such as coal, natural gas and petroleum. The technological advances in the 20th century made possible the extraction of fossil fuels from the earth commercially viable. All our modern transportation and industry development process have been made possible because of the discovery and extraction of fossil fuels. More than three quarters of the world's energy consumption comes from fossil fuels. Of this approximately, 40% of fossil fuels are used in petroleum form, 15 % in natural gas form and 8 % in coal form. Fossil fuels are the main backbone of the industrialization but they have contributed to the burden of environmental pollution significantly. This has resulted in greenhouse gases, acid rain and global climate change. The massive demand for fossil fuels has resulted in depletion of their deposits at an alarming rate..
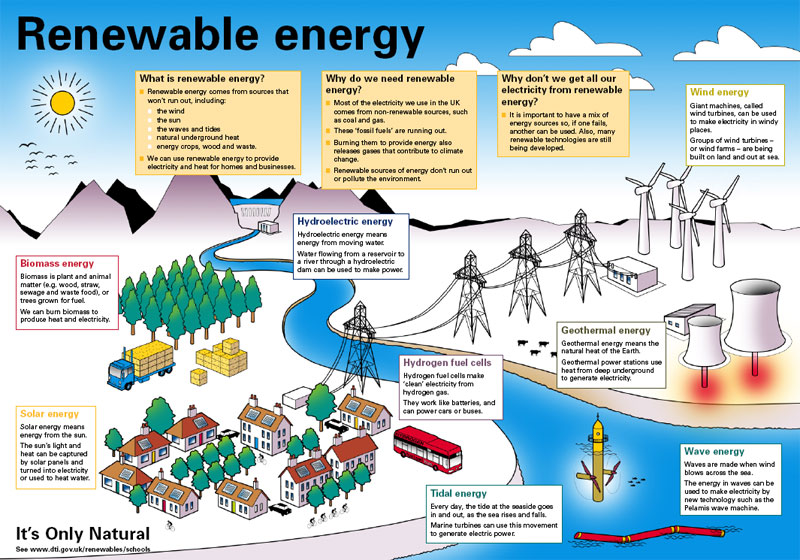
7.1.U2 Sources of energy with lower carbon dioxide emissions than fossil fuels include renewable energy (solar, biomass, hydropower, wind, wave, tidal and geothermal) and their use is expected to increase. Nuclear power is a low carbon low-emission non-renewable resource but is controversial due to the radioactive waste it produces and the potential scale of any accident.

Fossil fuels are nonrenewable, that is, they draw on finite resources that will eventually dwindle, becoming too expensive or too environmentally damaging to retrieve. In contrast, the many types of renewable energy resources are constantly replenished and will never run out.
Renewable energy plays an important role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. When renewable energy sources are used, the demand for fossil fuels is reduced. Unlike fossil fuels, non-biomass renewable sources of energy (hydropower, geothermal, wind, and solar) do not directly emit greenhouse gases.
Renewable energy resources are all sustainable as there is no depletion of natural capital. These resources can be large-scale for a whole country or small-scale for houses or communities.
Nuclear power is also considered a renewable energy source. It emits no greenhouse gases, acidic gases, or particulates - linked to, respectively, global warming, environmental degradation. The energy output of nuclear fission is the highest of any option today. This reduces both the use of natural resources. However, nuclear power poses numerous threats to people and the environment and point to studies in the literature that question if it will ever be a sustainable energy source. These threats include health risks and environmental damage from uranium mining, processing and transport, the risk of nuclear weapons proliferation or sabotage, and the unsolved problem of radioactive nuclear waste.
Renewable energy plays an important role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. When renewable energy sources are used, the demand for fossil fuels is reduced. Unlike fossil fuels, non-biomass renewable sources of energy (hydropower, geothermal, wind, and solar) do not directly emit greenhouse gases.
Renewable energy resources are all sustainable as there is no depletion of natural capital. These resources can be large-scale for a whole country or small-scale for houses or communities.
Nuclear power is also considered a renewable energy source. It emits no greenhouse gases, acidic gases, or particulates - linked to, respectively, global warming, environmental degradation. The energy output of nuclear fission is the highest of any option today. This reduces both the use of natural resources. However, nuclear power poses numerous threats to people and the environment and point to studies in the literature that question if it will ever be a sustainable energy source. These threats include health risks and environmental damage from uranium mining, processing and transport, the risk of nuclear weapons proliferation or sabotage, and the unsolved problem of radioactive nuclear waste.
7.1.U3 Energy security depends on adequate, reliable and affordable supply of energy that provides a degree of independence. An inequitable availability and uneven distributions of energy sources may lead to conflict.
 image from North Atlantic Treaty Organization
image from North Atlantic Treaty Organization
Energy security as the uninterrupted availability of energy sources at an affordable price. Energy security has many aspects: long-term energy security mainly deals with timely investments to supply energy in line with economic developments and environmental needs. On the other hand, short-term energy security focuses on the ability of the energy system to react promptly to sudden changes in the supply-demand balance.
Access to cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led to significant vulnerabilities. The Ukraine-Russia gas dispute in January 2009 caused the largest natural gas supply crisis in Europe’s history. With increasingly integrated electricity grids, blackouts can cascade and affect multiple economies simultaneously.
Access to cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led to significant vulnerabilities. The Ukraine-Russia gas dispute in January 2009 caused the largest natural gas supply crisis in Europe’s history. With increasingly integrated electricity grids, blackouts can cascade and affect multiple economies simultaneously.
7.1.U4 The energy choices adopted by a society may be influenced by availability; sustainability; scientific and technological developments; cultural attitudes; and political, economic and environmental factors. These in turn affect energy security and independence.
The choice of energy sources that a nation or society uses is very much dependent upon several factors. These include available energy resources, population size, historical energy use, needs of industry, available technology and political direction.
MEDCs have higher energy demands than LEDCs, as they depend on energy for transport, heating, air-conditioning, cooking and all other aspects of their lives
MEDCs have higher energy demands than LEDCs, as they depend on energy for transport, heating, air-conditioning, cooking and all other aspects of their lives
- Availability of the supply - domestic or international.
- Technology developments - does it already exist? Is there potential?
- Politics - can lead to conflict over supplies or choice to use domestic supplies at increased prices to reduce risk.
- Economics - cheaper to import or produce
- Cultural Attitudes - love of the SUV
- Sustainability
- Environmental Considerations - is it dangerous?
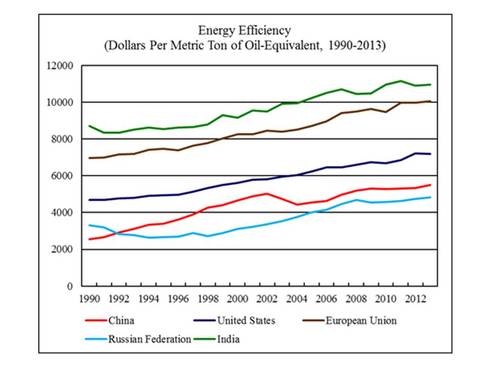
7.1.U5 Improvements in energy efficiencies and energy conservation can limit growth in energy demand and contribute to energy security.
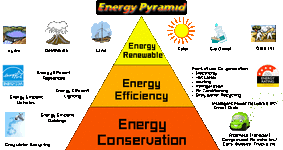 image from US Gas and Electric
image from US Gas and Electric
Energy efficiency has proved to be a cost-effective strategy for building economies without necessarily increasing energy consumption. Energy efficiency, is the goal to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. Reducing energy use reduces energy costs and may result in a financial cost saving to consumers if the energy savings offset any additional costs of implementing an energy efficient technology. Reducing energy use is also seen as a solution to the problem of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Enhanced environmental standards
- Reduced energy use and emission of carbon dioxide
- Reduction of waste
- Improved efficiency of walls and windows
- Energy-efficient appliances
- Improved building material
Applications and Skills
7.1.A1 Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources.
7.1.A2 Discuss the factors that affect the choice of energy sources adopted by different societies.
[Use case studies to highlight the energy choices of different countries]
[Use case studies to highlight the energy choices of different countries]
Factor that could affect the choice of energy
Availability
Availability
- Resources within or near to a country are better than those further away. The choice of what energy source should be used is different to countries. Some have large oil, coal and gas reserves. That makes fossil fuels an obvious choice for an energy source. The generation of energy also depends on its availability, economy, cultural, environmental and technological factors. When an energy resource is available and close, it is easier and efficient to use.
- If an energy source is more expensive than others, it would reduce the likelihood of it been chosen. Globally, renewable energy sources are not used as much. These resources are still not ready to meet current demands. Renewable sources can be used more if the production prices of the non-renewable sources are increased. This may better the environment as higher costs of the fossil fuels means that peoples view will change. Peoples interest in renewable resources has led to an increased demand for renewable and non-pollution sources. This leads to a greater investment and research into more alternatives or improvements.
- Culture fears based on the fear of nuclear accidents and waste, have made it quite unpopular to choose. Cultural and tradition means that non-renewable resources are favored, and the places with renewable energy resources are limited.
- If an energy source is harmful to the environment, some societies might not choose it. e.g Chernobyl disaster would cause USSR unlikely to choose nuclear energy.
- Higher technology may require expensive training of the workforce
7.1.A3 Discuss the factors which affect energy security.
For each of the factors below
Factors:
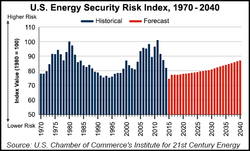
The energy security of a country can be measured using the ‘Energy Security Index’ (ESI).
This is based upon:
The higher the index, the lower the risk and therefore the greater the energy security
- identify one named example/country/location
- state whether energy security increased or decreased
- describe how the factor affected energy security
Factors:
- Supply and demand
- Total reserves
- Geopolitical development
- Climate change
- Physical – exhaustion of reserves or disruption of supply lines
- Environmental – Protests about environmental change caused by exploitation of energy resources
- Economic – sudden rises in costs of energy forcing increased imports of higher-priced energy
- Geopolitical – political instability in energy-producing regions
The energy security of a country can be measured using the ‘Energy Security Index’ (ESI).
This is based upon:
- Availability – the amount of a country’s domestic oil and gas supplies and its level of reliance on imported resources
- Diversity – the range of energy resources used
- Intensity – the degree to which the economy of a country is dependent on oil and gas
The higher the index, the lower the risk and therefore the greater the energy security
7.1.A4 Evaluate the energy strategy of a given society.

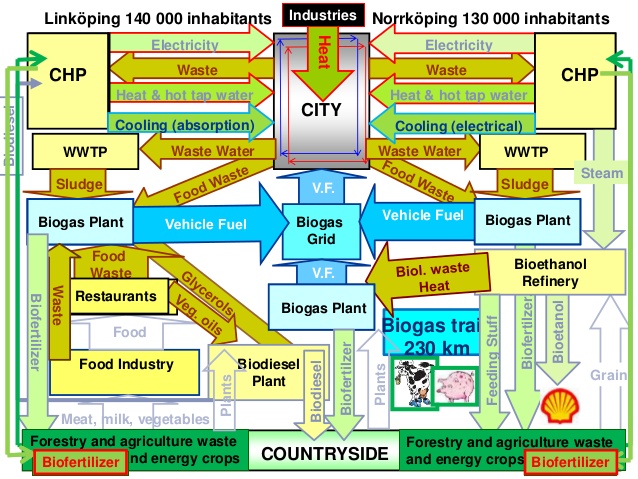
Energy use in Sweden is largely based on renewable energy. Thanks to cutting-edge technology and a wealth of natural assets, Sweden is in the front line as the world embarks on a shift to more sustainable energy systems. Few countries consume more energy per capita than Sweden, yet Swedish carbon emissions are low compared with those of other countries. According to the latest statistics from the International Energy Agency (IEA), the average Swede releases 4.25 tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO₂) per year into the atmosphere, compared with the EU average of 6.91 tonnes and the US average of 16.15 tonnes. Sweden has found a way to reduce emissions while the economy is growing.
Weigh the impact of each of the following factors on one country’s energy source
Weigh the impact of each of the following factors on one country’s energy source
- Supply and demand
- Total reserves
- Geopolitical developments
- Climate change
- Natural disasters
Key Terms
|
tidal
actual supply reserve energy security carbon emission natural gas |
solar
renewable potential supply production thermal efficiency low emission |
wind
non-renewable rate of consumption mineral resource sustainability energy independence |
hydro
nuclear economic depletion government subsidy |
geothermal
bio-fuel depletion time fracking fossil fuel coal |
Classroom Materials
Energy Sources Project
Energy Resources Case Study
Case Studies
France's Energy Change - Natural Gas Europe 3 Feb 2014
How 11 Countries Are Leading The Shift To Renewable Energy
Energy Sources Project
Energy Resources Case Study
Case Studies
- Detailed examples of the advantages and disadvantages of various energy sources, including: non-renewables (oil, coal, gas, nuclear) and renewables (solar, wind, hydro, tidal, biomass, geothermal)
- One detailed case study of the energy security and strategies of a given country (eg. Ethiopia, Denmark)
France's Energy Change - Natural Gas Europe 3 Feb 2014
How 11 Countries Are Leading The Shift To Renewable Energy
Powerpoint and Notes Adapted from Brad Kremer, Masfar
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
Correct use of terminology is a key skill in ESS. It is essential to use key terms correctly when communicating your understanding, particularly in assessments. Use the quizlet flashcards or other tools such as learn, scatter, space race, speller and test to help you master the vocabulary.
Useful Links
Fossil Fuels vs Renewable Energy from Ecology
Peak Oil Clock - Deans Corner
Fossil Fuel Formation
This interactive animation explains how photovoltaic panels convert sunshine to electricity.
Energyville Game - Chevron
Global Crisis Response Group on Food, Energy and Finance - UN Global Crisis Group
Fossil Fuels vs Renewable Energy from Ecology
Peak Oil Clock - Deans Corner
Fossil Fuel Formation
This interactive animation explains how photovoltaic panels convert sunshine to electricity.
Energyville Game - Chevron
Global Crisis Response Group on Food, Energy and Finance - UN Global Crisis Group
In The News
Harvesting ‘limitless’ hydrogen from self-powered cells - BBC Science and Environment News 20 September 2011
Himalayas could become the Saudi Arabia of solar - New Scientist Technology News 18 October 2011
Nuclear Power in France - World Nuclear Association Feb 2014
Here’s an article about natural gas production and populations of pronghorn antelope and elk in Wyoming, USA - New Scientist Environment News 4 May 2012
Plastics To Oil - NPR March 19, 2012
Inside the Fukashima Power Plant - BBC News 7 November 2013
Light From Plastic Bottles - wimp.com
Who Pays for Green of Germany - BBC News 27 February 2013
The use of palm oil for biofuel and as biomass for energy - Friends of the Earth
Port Augusta ‘busting a gut’ to reinvent itself as a solar city when coal-fired power is switched off” - Guardian on Mar.23, 2016,
Harvesting ‘limitless’ hydrogen from self-powered cells - BBC Science and Environment News 20 September 2011
Himalayas could become the Saudi Arabia of solar - New Scientist Technology News 18 October 2011
Nuclear Power in France - World Nuclear Association Feb 2014
Here’s an article about natural gas production and populations of pronghorn antelope and elk in Wyoming, USA - New Scientist Environment News 4 May 2012
Plastics To Oil - NPR March 19, 2012
Inside the Fukashima Power Plant - BBC News 7 November 2013
Light From Plastic Bottles - wimp.com
Who Pays for Green of Germany - BBC News 27 February 2013
The use of palm oil for biofuel and as biomass for energy - Friends of the Earth
Port Augusta ‘busting a gut’ to reinvent itself as a solar city when coal-fired power is switched off” - Guardian on Mar.23, 2016,
International Mindedness
- Choice of energy sources can have impacts at both local and global level as emissions of greenhouse gases can contribute to global climatic change.
- Political and economic situations around the world can affect energy security and choice of options.
TOK:
Video Clip
- The choice of energy sources is controversial and complex—how can we distinguish between a scientific claim and a pseudoscience claim when making choices?
Video Clip
Fossil fuels have powered human growth and ingenuity for centuries. Now that we're reaching the end of cheap and abundant oil and coal supplies, we're in for an exciting ride. While there's a real risk that we'll fall off a cliff, there's still time to control our transition to a post-carbon future.
Energy is neither created nor destroyed — and yet the global demand for it continues to increase. But where does energy come from, and where does it go? Joshua M. Sneideman examines the many ways in which energy cycles through our planet, from the sun to our food chain to electricity and beyond.
Today, we consume a truly vast amount of energy - with demand continuing to skyrocket at an alarming rate. We know that producing this energy has significant environmental impacts and emitting so much carbon dioxide into the atmosphere could cause catastrophic climate change
How much land mass would renewables need to power a nation like the UK? An entire country's worth. In this pragmatic talk, David MacKay tours the basic mathematics that show worrying limitations on our sustainable energy options and explains why we should pursue them anyway
Blind Spot is a documentary film that illustrates the current oil and energy crisis that our world is facing. Whatever measures of ignorance, greed, wishful thinking, we have put ourselves at a crossroads, which offer two paths with dire consequences.
Bill Gates talks about the future of energy usage and his investments in alternatives to fossil fuels.
Anything with the word nuclear next to it usually comes with a fair bit of misunderstanding. Hopefully this video demystifies the process of how nuclear fuels are turned into electricity and how we can use them in combination with renewables in order to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and the effects on the climate that come with high levels of them.
For the Baltic States, the pursuit of energy independence is about more than reliable energy sources – it’s about political freedom. In today’s security context, many dimensions of energy security have become increasingly important.
How Germany got stuck paying for Russia's war.
This episode stars Nobel Peace Prize-winner Muhammad Yunus, who founded the Grameen Shakti organization in Bangladesh distributes small solar systems and portable bio-gas systems to rural Bangladeshis, empowering women and the poor in the process
The United Kingdom: Case Study