topic 2.2: water

In the Water unit students are introduced to the structure and function of water, as the medium of life. Water has many useful properties, and so it is ubiquitous in life on earth. The useful properties of water arise from its structure.
The unit is planned to take 2 school days
The unit is planned to take 2 school days
Essential idea:
- Water is the medium of life.
Nature of science:
- Use theories to explain natural phenomena—the theory that hydrogen bonds form between water molecules explains the properties of water.
- State why scientists cannot prove without a doubt that hydrogen bonds exist between water molecules.
- State why scientists cannot prove without a doubt that hydrogen bonds exist between water molecules.
Understanding:
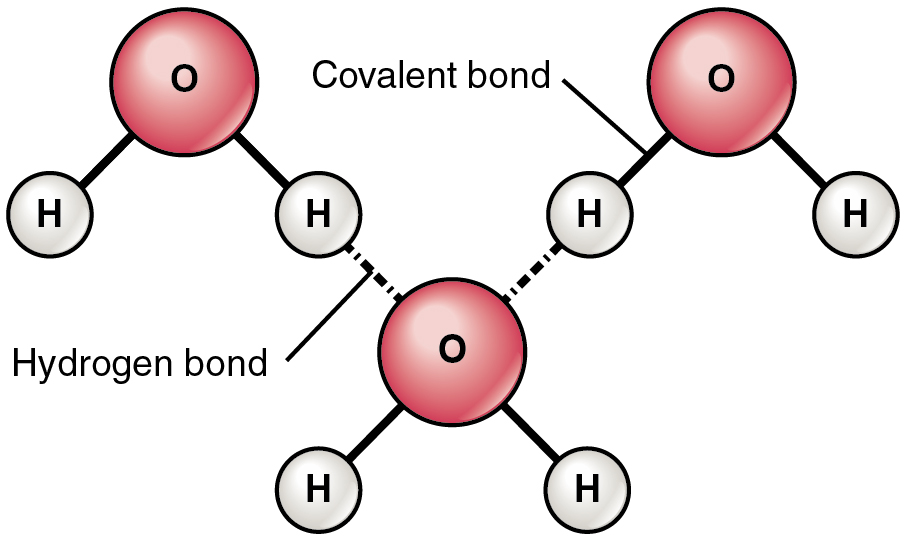
2.2.U.1 Water molecules are polar and hydrogen bonds form between them (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 68).
- Describe the structure of an atom (in terms of protons, neutrons and electrons).
- Contrast ion with atom.
- Define anion and cation.
- Contrast covalent, ionic and hydrogen bonds.
- Write the molecular formula for water and draw the atomic structure of the molecule.
- Describe the cause and effect of the polar nature of water.
- Describe where and how water is able to form hydrogen bonds.
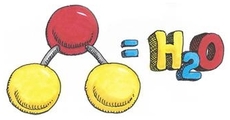 image from http://www.whatischemistry.unina.it/
image from http://www.whatischemistry.unina.it/
Water molecule formed by hydrogen bonds between oxygen and hydrogen. However sharing of electrons is unequal and are attracted to the oxygen more. Partial negative charge develops on the oxygen and partial positive on the hydrogen. Attraction between water molecules forms a hydrogen bond and forms when a hydrogen atom in one polar molecule is attracted to the slightly negative oxygen atom in the other molecule.
A water molecule consists of an oxygen atom covalently bound to two hydrogen atoms. Since O is more electronegative than H, an unequal sharing of electrons occurs. This creates a polar covalent bond with H having a partial positive charge and O having a partial negative charge.
Water is also bent so the positive charge exists more or less on one side and the negative charge from the O exists on the opposite side. The partial +ve charge is attracted to the partial –ve charge creating an intermolecular attraction between the water molecules called a “Hydrogen bond.”. H-bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular bonding, but is still considered a weak bond; however since there are so many H2O molecules they give water its unique properties and make it essential to life on this planet
A water molecule consists of an oxygen atom covalently bound to two hydrogen atoms. Since O is more electronegative than H, an unequal sharing of electrons occurs. This creates a polar covalent bond with H having a partial positive charge and O having a partial negative charge.
Water is also bent so the positive charge exists more or less on one side and the negative charge from the O exists on the opposite side. The partial +ve charge is attracted to the partial –ve charge creating an intermolecular attraction between the water molecules called a “Hydrogen bond.”. H-bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular bonding, but is still considered a weak bond; however since there are so many H2O molecules they give water its unique properties and make it essential to life on this planet
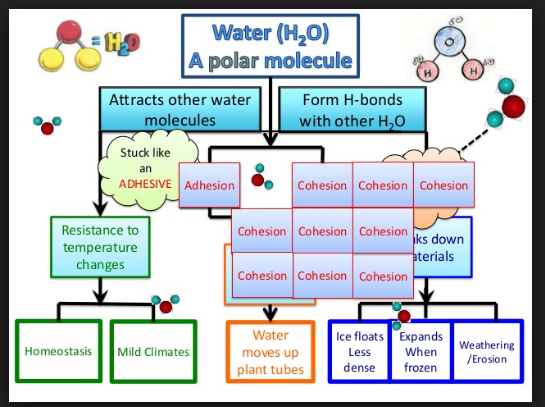
2.2.U.2 Hydrogen bonding and dipolarity explain the cohesive, adhesive, thermal and solvent properties of water (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 69).
- Contrast adhesion with cohesion.
- Outline an example of the cohesive property of water being of benefit to life.
- Outline an example of the adhesive property of water being of benefit to life.
- Explain three thermal properties of water that are useful to living organisms.
- Outline a benefit to life of water's high specific heat capacity.
- Outline a benefit to life of water's high latent heat of vaporization.
- Outline a benefit to life of water's high boiling point.
- Explain why is water such a good solvent.
- List the types of molecules that water will dissolve.
cohesion
adhesion
thermal properties
solvent properties
- hydrogen bonds between polar water molecules cause them to cohere
- allowing for transpiration in plants moving water against gravity
- surface tension between cohering water molecules
- allowing for animals such as water striders to walk over the surface of ponds even though they are denser than water
adhesion
- hydrogen bonds between polar water molecules and any other charged or ionic substance cause them to cohere
- allowing for transport in an aqueous environment
thermal properties
- hydrogen bonds between polar water molecules cause water to resist change
- high specific heat (energy required to change water temperature)
- high heat of vaporization (energy required to boil water)
- high heat of fusion (loss of energy required to freeze water)
- thus, water produces a stable environment for aquatic organisms
solvent properties
- the polarity of water attracts, or dissolves, any other polar or charged particles by forming hydrogen bonds with them
- proteins, glucose, or ions, such as sodium or calcium are all soluble
- cytoplasm is primarily water, providing a polar medium in which other polar or charged molecules dissolve
- many enzymes are globular proteins that are water soluble so they dissolve in cytoplasm where they control metabolic reactions
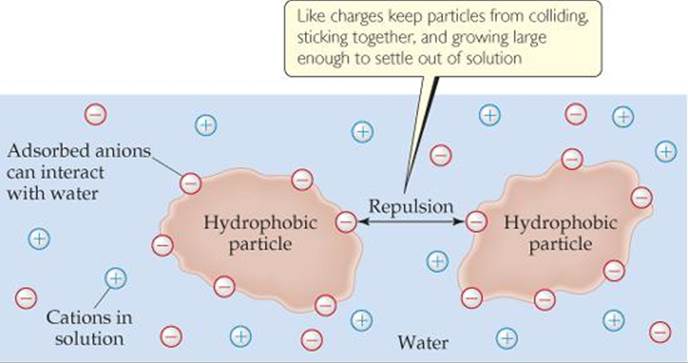
2.2.U.3 Substances can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 70).
- State that polar and ionic molecules are hydrophilic.
- State that non-polar, non-ionic molecules are hydrophobic.
- Given a diagram of a molecular structure, determine if the molecule is hydrophilic or hydrophobic.
 image from http://www.buzzle.com
image from http://www.buzzle.com
Hydrophilic - A substance that has an affinity for water. These substances can interact or be dissolved by water.(Ex. Like Dissolves Like, detergents, alcohols, salts, cotton,)
Hydrophobic - substances that repel to water. They are non-polar and interact well with other non-polar solvents. An example could be molecules are hydrophobic if they don’t have positive or negative charges
Hydrophobic - substances that repel to water. They are non-polar and interact well with other non-polar solvents. An example could be molecules are hydrophobic if they don’t have positive or negative charges
Application:
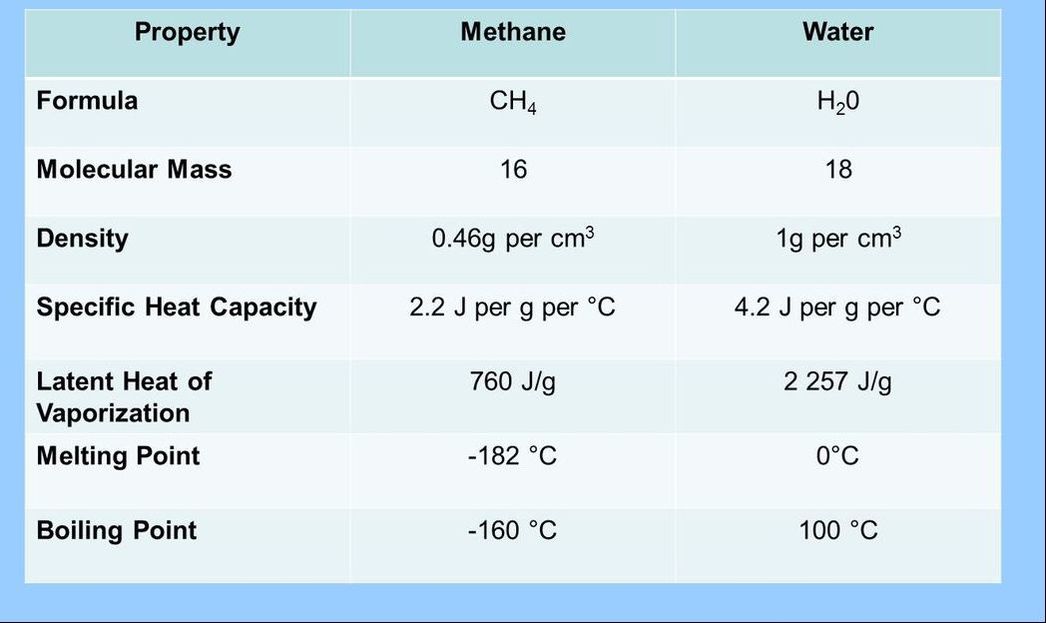
2.2.A.1 Comparison of the thermal properties of water with those of methane. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 71).
- Compare and contrast the physical properties of methane and water.
- Explain why water and methane have different thermal properties based on their molecular structures.
2.2.A.2 Use of water as a coolant in sweat (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 72).
- Explain sweating as a mechanism to cool the body.

Water can evaporate at temperatures below the boiling point. Hydrogen bonds need to break for this to occur. The evaporation of water cools body surfaces by using the energy from liquid water to break the hydrogen bonds. Sweat uses evaporative cooling to maintain body temperature. As liquids evaporate, they shed molecules into the air. The liquid changes into a gas, drawing heat from the liquid. The process draws heat from the body. Evaporation also cools the remaining liquid because faster-moving hot molecules are more likely to escape into the air.
2.2.A.3 Modes of transport of glucose, amino acids, cholesterol, fats, oxygen and sodium chloride in blood in relation to their solubility in water. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 72).
- State if the following molecules are hydrophobic or hydrophilic: glucose, amino acids, cholesterol, fats, oxygen, and sodium chloride.
- Outline the mechanism of transport in the blood of the following molecules: glucose, amino acids, cholesterol, fats, oxygen, and sodium chloride.
The solvent properties of water mean that many different substances can dissolve in it because of its polarity. This allows substances to be carried in the blood and sap of plants as they dissolve in water. It also makes water a good medium for metabolic reactions.
- Sodium chloride: ions which dissolve and travel through the blood
- Amino acids: Polar and soluble, depending on the R group, soluble enough to be dissolved in blood plasma
- Glucose: polar and freely soluble hence carried through blood plasma
- Oxygen: Non polar but small enough to dissolve in water in very small amounts that is not enough to satisfy aerobic respiration. Haemoglobin present as binding sites for oxygen.
- Fats molecules: Entirely non polar and travel inside lipoprotein complexes which have a single layer of phospholipid also containing proteins.
- Cholesterol: Hydrophobic and are carried via lipoprotein complexes with their hydrophilic region facing outwards
Key Terms:
|
element
trace element matter proton neutron electron metabolic reaction coolant vaporization |
covalent
polar ionic ion cation carbohydrate lipid polarity thermal |
anion
hydrogen bond organic monomer polymer carbon hydrogen sodium iron |
condensation
hydrolysis hydrophobic hydrophilic adhesion oxygen nitrogen phosphorous |
density
capillary action solvent surface tension nucleic acid protein sulfur calcium |
Classroom Material:
Water
Characteristics of Water (ppt)
Characteristics of Water (notes)
Water Demo lab
Properties of water review
Water worksheet
Water Table
Topic 2.2 Review
Topic 2.2 Kahoot Review Quiz
Water
Characteristics of Water (ppt)
Characteristics of Water (notes)
Water Demo lab
Properties of water review
Water worksheet
Water Table
Topic 2.2 Review
Topic 2.2 Kahoot Review Quiz
Powerpoint and Study Guide by Chris Payne
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
Correct use of terminology is a key skill in Biology. It is essential to use key terms correctly when communicating your understanding, particularly in assessments. Use the quizlet flashcards or other tools such as learn, scatter, space race, speller and test to help you master the vocabulary.
Useful Links:
Water
Animated Bonds
Hydrogen Bonds and Water
Structure of Water
The Chemistry of Water
Phases of Water
Water properties and behavior
Salt Dissolving in Water
Water balloons in space
Water properties and behavior
Simple H-bonds from John Gianni
H-bonds in water, from Northland College
Properties of water, from Northland College
Molecule polarity simulation from PhET Labs (allow Java to run)
Solubility in water simulation from PhET Labs (allow Java to run)
Dissolving, from Northland College
Dissolving NaCl from PreparatoryChemistry
PhET Labs: Salts and Solubility and also Dissolving Sugars and Salts
Click here and access a good primer on the properties of water. Insert express code 4273P and click on Weblink 3.1
In the News:
International-mindedness:
- There are challenges for the increasing human population in sharing water resources equitably for drinking and irrigation, electricity generation and a range of industrial and domestic processes.
TOK
- Claims about the “memory of water” have been categorized as pseudoscientific. What are the criteria that can be used to distinguish scientific claims from pseudoscientific claims?
Video Clips
Hank teaches us why water is one of the most fascinating and important substances in the universe.
Explore some properties of water with the Amoeba Sisters! It's all about those hydrogen bonds. Terms discussed include adhesion, cohesion, surface tension, specific heat - all made possible by those amazing hydrogen bonds.
Water is both essential and unique. Many of its particular qualities stem from the fact that it consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen, therefore creating an unequal sharing of electrons. From fish in frozen lakes to ice floating on water, Christina Kleinberg describes the effects of polarity.
In this video Paul Andersen explains how the polarity of water makes life on the planet possible. Oxygen is highly electronegative and pulls the electrons closely creating a partial negative charge. The polarity of water (and the corresponding hydrogen bonds) create cohesion, adhesion, capillary action, high specific heat, and a universally good solvent.
Water is essentially everywhere in our world, and the average human is composed of between 55 and 60% water. So what role does water play in our bodies, and how much do we actually need to drink to stay healthy? Mia Nacamulli details the health benefits of hydration
The diving bell spider uses surface tension and a little bit of web-egineering to build a bubble to allow it to live and exchange gases underwater.
How does water behave in zero gravity? Find out at the international space station (this is really good):