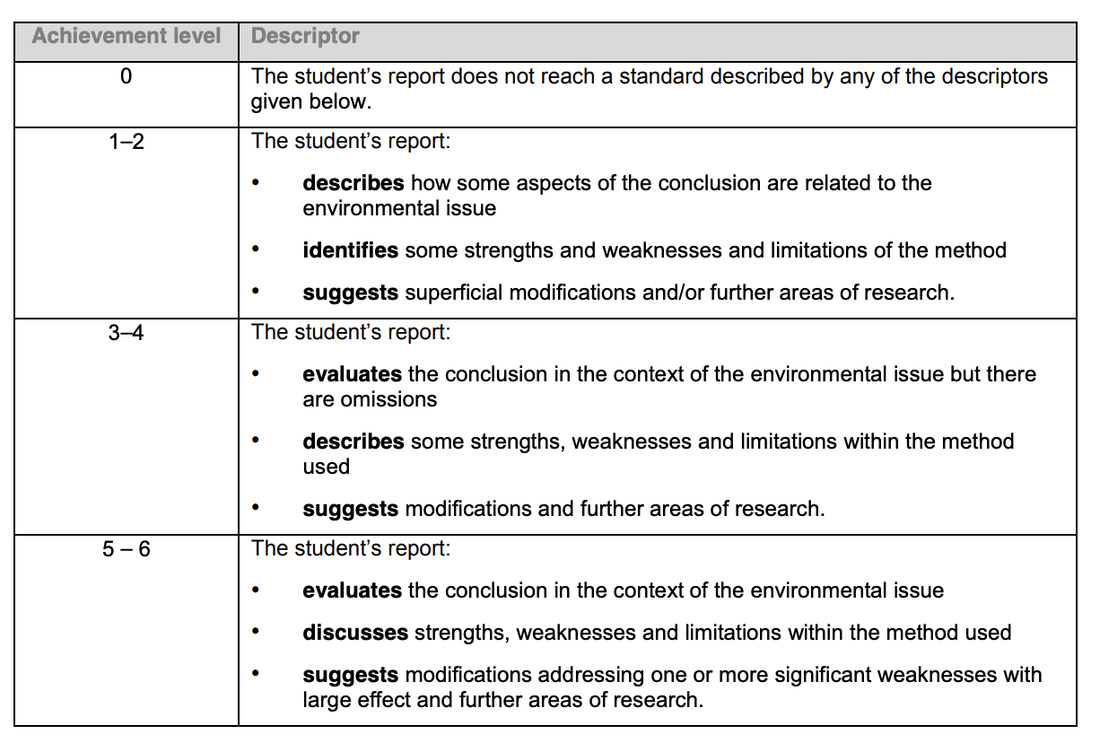
discussion & evaluation
 image from clipart-library.com
image from clipart-library.com
This criterion assesses the extent to which you discuss the conclusion in the context of the environmental issue, and carries out an evaluation of the investigation.
This criterion requires you to reflect on your study. In the first instance, you should evaluate the methodology of your research, discussing the strengths, weaknesses and limitations of the process. Any research project at this level is likely to be influenced by limitations, and the focus here is to identify these and to reflect on how they have impacted on the conclusion of the study. It might also be that weaknesses in the experimental design that became evident as a result of carrying out the study are discussed here. It is worth noting that although there is no requirement that the report is organized according to the headings of the criteria, consideration of the validity of the data will be assessed as part of the conclusion, and evaluation of the methodology will be assessed in this discussion criterion.
You must also reflect on the outcomes of your investigation in relation to the broader environmental issue, which was raised at the beginning of the internal assessment process. To what extent do your findings support or contrast with information available in the literature? What reasons can you suggest for any similarities or differences? It is at this stage that the focused research question is now widened to re-address the broader environmental issue or concern.
This criterion requires you to reflect on your study. In the first instance, you should evaluate the methodology of your research, discussing the strengths, weaknesses and limitations of the process. Any research project at this level is likely to be influenced by limitations, and the focus here is to identify these and to reflect on how they have impacted on the conclusion of the study. It might also be that weaknesses in the experimental design that became evident as a result of carrying out the study are discussed here. It is worth noting that although there is no requirement that the report is organized according to the headings of the criteria, consideration of the validity of the data will be assessed as part of the conclusion, and evaluation of the methodology will be assessed in this discussion criterion.
You must also reflect on the outcomes of your investigation in relation to the broader environmental issue, which was raised at the beginning of the internal assessment process. To what extent do your findings support or contrast with information available in the literature? What reasons can you suggest for any similarities or differences? It is at this stage that the focused research question is now widened to re-address the broader environmental issue or concern.
Discussion and evaluation (6)
Discussion
You are required to evaluate your conclusion with respect to your Research Question and Environmental Issue.
It is at this stage that the focused research question is now widened to re-address the broader environmental issue or concern.
Evaluation
Evaluate the methodology of your research,
Limitations:
The design and method of the investigation must be commented upon as well as the quality of the data.
Identify and discuss significant errors and limitations that could have affected the outcome of the experiment.
Emphasis in this section should be on systematic errors, not the random errors that always occur in reading instruments and taking measurements. Identify the source of error and if possible, tie it to how it likely affected the results.
Acceptable Example:
“Because the simple calorimeter we used was made from a tin can, some heat was lost to the surroundings—metals conduct heat well. Therefore, the value we obtained for the heat gained by the water in the calorimeter was lower than it should have been.”
Unacceptable Examples:
You must not only list the weaknesses but must also appreciate how significant the weaknesses are. Comments about the precision and accuracy of the measurements are relevant. When evaluating the procedure used, the specifically look at the processes, use of equipment and management of time.
RULE OF THUMB: Every error/ weakness addressed needs and effect on the data and a specific improvement
Suggestions:
Suggestions for improvements should be based on the weaknesses and limitations identified.
Modifications to the experimental techniques and the data range can be addressed here. The modifications proposed should be realistic and clearly specified. Suggestions should focus on specific pieces of equipment or techniques used.
It is not sufficient to state generally that more precise equipment should be used. Vague comments such as “I should have worked more carefully” are not acceptable.
Discussion
You are required to evaluate your conclusion with respect to your Research Question and Environmental Issue.
- reflect on the outcomes of your investigation in relation to the broader environmental issue, which was raised at the beginning of the internal assessment process.
- to what extent do your findings support or contrast with information available in the literature? What reasons can they suggest for any similarities or differences?
It is at this stage that the focused research question is now widened to re-address the broader environmental issue or concern.
Evaluation
Evaluate the methodology of your research,
- discuss the strengths, weaknesses and limitations of the impacted on the conclusion
- discuss weaknesses in the experimental design that became evident as a result of carrying out your study
- validity of the data will be assessed as part of the conclusion, and evaluation of the methodology will be assessed in this discussion criterion.
Limitations:
- The variation in results is reported, showing the strength of the conclusion.
- The appropriateness of the apparatus in obtaining relevant data is commented on.
- Weaknesses in the methodology are discussed.
- The reliability of the data is commented on.
- The quantity of the data is commented on (both MV and RV).
- The precision, accuracy and uncertainty in the data is commented on.
- Outlier data or irregularities in the data are addressed.
The design and method of the investigation must be commented upon as well as the quality of the data.
- consider how large your errors or uncertainties are in the results.
- how confident are you in the results
- are you fairly conclusive, or are other interpretations/results possible
Identify and discuss significant errors and limitations that could have affected the outcome of the experiment.
- were there important variables that were not controlled?
- were there flaws in the procedure which could affect the results?
- are measurements and observations reliable?
- was there a lack of replication?
Emphasis in this section should be on systematic errors, not the random errors that always occur in reading instruments and taking measurements. Identify the source of error and if possible, tie it to how it likely affected the results.
Acceptable Example:
“Because the simple calorimeter we used was made from a tin can, some heat was lost to the surroundings—metals conduct heat well. Therefore, the value we obtained for the heat gained by the water in the calorimeter was lower than it should have been.”
Unacceptable Examples:
- "The test tubes weren’t clean.”
- “Human error.”
You must not only list the weaknesses but must also appreciate how significant the weaknesses are. Comments about the precision and accuracy of the measurements are relevant. When evaluating the procedure used, the specifically look at the processes, use of equipment and management of time.
RULE OF THUMB: Every error/ weakness addressed needs and effect on the data and a specific improvement
Suggestions:
- Where limitations are determined to be significant, specific improvements are proposed.
- Improvements effectively and specifically address the limitations.
- Improvements are given which are possible within the context of a school laboratory.
- An addition research question is stated with clear IV and DV.
- The research questions are an extension from the conclusion and evaluation.
- A short explanation for the question is given to establish its importance and relevance.
Suggestions for improvements should be based on the weaknesses and limitations identified.
Modifications to the experimental techniques and the data range can be addressed here. The modifications proposed should be realistic and clearly specified. Suggestions should focus on specific pieces of equipment or techniques used.
It is not sufficient to state generally that more precise equipment should be used. Vague comments such as “I should have worked more carefully” are not acceptable.
Discussion and Evaluation Rubric