option c.1: (core) species and communities

Essential idea:
- Community structure is an emergent property of an ecosystem.
Nature of science:
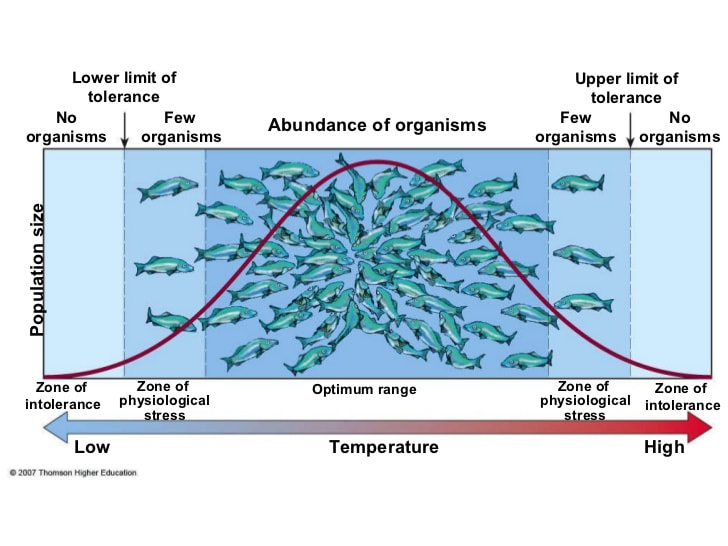
- Use models as representations of the real world—zones of stress and limits of tolerance graphs are models of the real world that have predictive power and explain community structure. (1.10)
Understandings
C 1.1 U The distribution of species is affected by limiting factors.
- Define community
- Define abiotic
- Define biotic
- Define limiting factor
- Outline how temperature, water, light, soil pH, salinity and mineral nutrients affect the distribution of plant species
- Outline how temperature, water, breeding sites, food supply and territories affect the distribution of animal specie
C 1.U2 Community structure can be strongly affected by keystone species.
- Describe the importance of keystone species to a community
- List two examples of keystone species
C 1.3 U Each species plays a unique role within a community because of the unique combination of its spatial habitat and interactions with other species.
C 1.U4 Interactions between species in a community can be classified according to their effect.
C 1.U5 Two species cannot survive indefinitely in the same habitat if their niches are identical.
Application
C 1.A1 Distribution of one animal and one plant species to illustrate limits of tolerance and zones of stress.
C 1.A2 Local examples to illustrate the range of ways in which species can interact within a community.
C 1.A3 The symbiotic relationship between Zooxanthellae and reef-building coral reef species.
Skills
C 1.S1 Analysis of a data set that illustrates the distinction between fundamental and realized niche.
C 1.S2 Use of a transect to correlate the distribution of plant or animal species with an abiotic variable.
- Outline why sampling must be random.
- Explain methods of random sampling, including the use of a transect
- State the null and alternative hypothesis of the chi-square test of association.
- Use a contingency table to complete a chi-square test of association.
Key Terms
Classroom Assignments:
Useful Links
In the News
Theory of knowledge:
- Random samples are taken in studies involving large geographical areas or if limited time is available. Is random sampling a useful tool for scientists despite the potential for sampling bias?
Video Clips
When wolves were reintroduced to Yellowstone National Park in the United States after being absent nearly 70 years, the most remarkable "trophic cascade" occurred. What is a trophic cascade and how exactly do wolves change rivers? George Monbiot explains in this movie remix
What do gray wolves, elephants, and parrotfish have in common? They're all keystone species, which means they have an especially large impact on their habitat. SciShow explores how these animals keep their ecosystems running.
Paul Andersen explains how ecosystems interact with biotic and abiotic factors. He explains and gives examples of food chains and food webs. He shows how limiting factors eventually leads to logistic growth. Real data from Yellowstone Park is used to show how populations interact. He ends the podcast by showing how human impacts can eventually lead to changes within an ecosystem.
Paul Andersen explains the niche. He gives three different pronunciations and two different definitions. He then discusses the competitive exclusion principle and the idea that a niche cannot be shared by two species.
Paul Andersen explains the major classification terms in ecology and how a community can be measured by species composition and species diversity. The symbiosis of leaf cutter ants is included. The podcast ends with a discussion of population growth.
How many African elephants are left and where are they? This video follows the work of researchers conducting the first census of African savanna elephants in over 40 years and the methods they are using to obtain accurate, up-to-date numbers across the continent.
Biologists Piotr Naskrecki and Jennifer Guyton identify and record the diversity of species in Gorongosa National Park’s Cheringoma Plateau.
Today we're going to be exploring various sampling strategies including the use of quadrats. It's usually not possible to look at every single individual of a species within a given area. It's also pretty rare that you'll be able to look at every single square meter within that area too.
GCSE Biology Revision: Sampling along a transect